This section describes the Spot management optimization solution.
Many AWS users do not maximize the cost savings of Spot instances due to concerns about interruptions—such as Pod eviction, delayed rescheduling, and potential downtime. The result: overreliance on expensive On-Demand nodes.
Kompass Spot management mitigates these risks using HiberScale technology. Hibernated, prewarmed nodes are ready to resume immediately if a Spot instance is interrupted, allowing evicted Pods to restart well before the 2-minute instance termination.
Kompass also classifies which workloads are suitable for Spot, based on the application configuration and reduced start time. This way, you can safely migrate suitable workloads away from On-Demand without compromising performance.
This combination of rapid resume time and proactive workload protection makes Spot safer:
Protects workloads from Spot interruption without impacting SLA.
Identifies and safely migrates eligible workloads to Spot—reducing dependency on costly On-Demand instances.
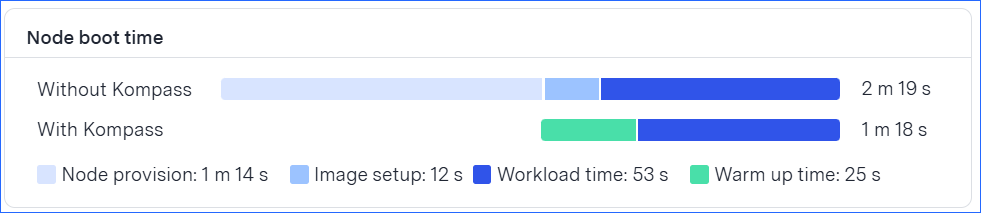
The following figure illustrates how the faster boot time of Kompass nodes enables evicted Pods to be rescheduled and running before the Spot instance is terminated:
As recommended by Kubernetes and by AWS best practices, you should configure a Pod Disruption Budget (PDB) to limit the number of Pods that can become simultaneously unavailable. A PDB helps ensure that a minimum number of Pods remain available even during the 2 minute notification time of a Spot interruption.
Pods kept available by the PDB can then be quickly rescheduled to the Kompass nodes before termination.
During large-scale Spot interruptions, the combination of PDB enforcement and rapid node provisioning ensures there is no application downtime.
For this reason, Spot management can be activated only on workloads that have a PDB configured.
If you attempt to activate Spot management for a workload without a PDB, Kompass displays code that you can use to configure it for that workload.
Alternatively, you can use this generic code.
Change the environment variables as needed:
apiVersion: policy/v1
kind: PodDisruptionBudget
metadata:
name: "{{ .Values.deployment.name }}-pdb"
spec:
maxUnavailable: 20%
selector:
matchLabels:
service: "{{ .Values.deployment.name }}"For more information, see this Kubernetes documentation: Specifying a Disruption Budget for your Application.
The Spot management solution relies on two Kompass agents installed on a cluster:
The Kompass Insights agent is installed.
This agent provides visibility into the workloads running in the cluster.
It can take up to 7 days after installing the agent for Kompass to deliver accurate recommendations.The Kompass Compute agent is installed
When this agent is installed, you can apply the Spot management (and Headroom reduction) solution to workloads..
It can take up to 1 hour after installing the Compute agent before you can apply the solution to workloads.
For more information, see Deploy Kompass Compute.
In addition, PDB must be configured for the workload.
See also: